
Note: MTR is not only available on Linux, but also on Windows ( winMTR) and on Mac.Īs with other traceroute tools, mtr relies on ICMP Time Exceeded packets coming back from the transit hops/routers, by sending ICMP Echo request packets with the time to live (TTL) field increasing by one for each request. It allows you to constantly poll a remote host and see how the latency, packet lost ratio, and jitter changes over time. My traceroute, originally named Matt’s traceroute ( MTR) combines the functionalities of a ping, to measure latency, jitter, packet loss, and a traceroute, to see the path and number of hops between the sender and destination, in the same tool.

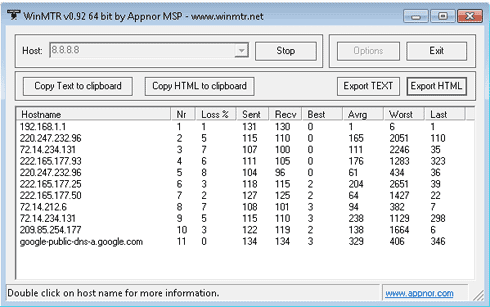
In replacement of steps 4 and 5 above, we can use the mtr command. Then, we make a traceroute to see the path we use to reach this destination? – To see the routing path and hops to this destination.Can we ping the destination on another network? – To check if the routing to the destination is working, and to also have an idea of the RTT and packet lost ratio.Can we ping our gateway? – To check the layer-3 part of our local network.Can we ping another host on the same network? – To check the layer-2 part.Can we ping our own IP address? – To check if our own IP is correct and if the interface is up.We all know the ping and traceroute commands to make the basic network debugging tasks from a host.įor example, if we use a down-up method to troubleshoot connectivity to a remote host: Ping and traceroute for basic network troubleshooting
#Mtr traceroute series
This post is part of a series of basic Linux Networking tips and tricks. In this post, I will talk about the Linux mtr command.

Here is the second post of the series on basic network troubleshooting and tools under RHEL / CentOS.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
